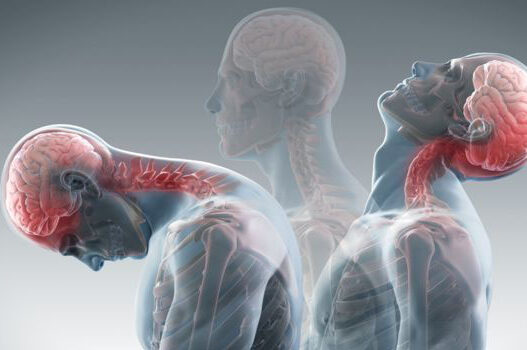
Whiplash
is caused by an abrupt backward and/or forward jerking motion of the head. This can be caused as a result of a car accident, riding accident or a fall.
The pain may be felt immediately but in many cases it may be delayed for 24hrs or more.
The symptoms
The symptoms that are felt can vary but generally include:
- Neck pain and stiffness
- Headaches- these may vary from being around the base of the skull radiating up over the head or just across the forehead.
- Pain around the back of the shoulders and may radiate towards the shoulder blades.
- Pain or numbness may radiate down the arm and into the hand
- Dizziness
- Other symptoms may also be difficulty concentrating, general fatigue, irritability and being over emotional
- Sleep may be disturbed
- In some cases the pain may extend down into the lower back
- Tinnitus or ringing in the ears can sometimes occur
Diagnosis
Most cases of whiplash just cause injury to the soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments and discs so damage to them will not show up on an X ray. A standard Xray is very useful to diagnose or rule out any fracture. If needed an MRI will show the damage to the discs.
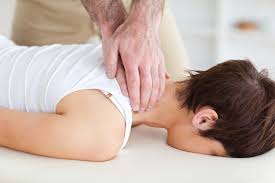
Treatment
This is currently aimed at :
1. Pain relief
2. Encouraging early movement with some simple exercises under the supervision of a physiotherapist
3. Physiotherapy– as above the gentle mobilising techniques used by the physiotherapist can ease the painful stiff joints and can also have a relaxing effect on the deep muscle spasm.
If the pain is extreme the physiotherapist may use traction, massage, heat and ice. The patient might also be offered a soft collar for a very limited time as the current thinking is that immobilising the neck is not a good solution.
The physiotherapist will also show you ways to make yourself comfortable at night or suggest a certain type of pillow.
Prognosis
Most patients with whiplash will see the majority of their symptoms subside in around a month. In a few cases symptoms can persist for a period of 6 months or more. This is called chronic whiplash. In these cases the dosage of painkillers may be increased and maintaining neck mobility will still be the focus of treatment. A doctor may recommend a course of anti-depressants should any signs of anxiety or depression appear.