Urine infections -are much more common in women than men but as men get older and have enlarged prostrate glands they are also vulnerable to infections.
Infections are caused by bacteria invading and multiplying in the bladder and sometimes the kidneys plus the tubes that drain urine from the kidney to the bladder.Correct diagnosis is key to a swift recovery and common antibiotics are prescribed
Signs and Symptoms of UTIs
The symptoms of a bladder infection tend to come on quite quickly and include:
- painful urination and a burning sensation
- needing to urinate frequently
- sudden urges to empty your bladder, called urinary urgency
- pain in your central lower abdomen, just above the pubic bone
- there may be blood in your urine
In more severe cases when the kidneys involved there may also be
- pain in your lower back that may radiate some way up but does not alter when you change position
- fever and shaking with cold (usually indicating a fever)
- nausea and vomiting
If the cause is a prostate infection you may also experience
Fever
Feeling tired
Difficulty urinating and some dribbling
You may have pelvic pain
Causes of UTIs
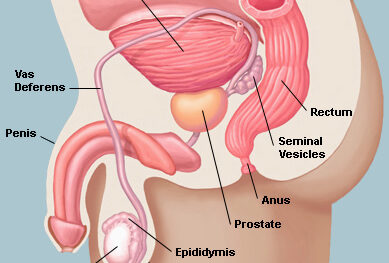
Most UTIs are caused by a bacterial infection where the bacteria E. coli, which is naturally present in your body gets into the urinary tract through the urethra. The urethra is the tube that drains urine from your bladder through your penis.
UTIs are more common in women than in men because their urethra is shorter and the bacteria need to travel a shorter distance to reach their bladder.
UTIs in men are more common with older age. One reason is that older men are more likely to develop noncancerous enlargement of their prostate gland.
The prostate wraps around the neck of the bladder, where the urethra connects to the bladder. Enlargement of the prostate gland can choke off the bladder neck, making it harder for urine to flow freely. If the bladder does not empty completely, bacteria that are normally flushed out with the urine might gain a foothold.
Other factors that can put you at greater risk for UTIs especially as you get older are:
Being immobile for long periods
Not drinking enough fluids
Recent urinary tract surgery
Wearing pads and not changing them regularly
Poor hygiene
People with Diabetes also have a higher incidence of UTI
Diagnosing UTIs
The GP will ask about your symptoms, past history and may want a sample.
They will ask check to see if you have an enlarged prostrate gland.
If you are in acute problems contact them as a matter of urgency or contact 111
Treatment for UTIs
If the test comes back positive for an infection you will need antibiotic tablets. Depending on the type of antibiotic your doctor prescribes, you will take the pills either once or twice a day for five to seven or more days.
Also it is very important to drink enough fluids even if urinating is painful as this helps flush out the bacteria.
It is very important to take the full course of antibiotics even if you feel better or the infection could come back and become more resistant to the antibiotic.
Prevention
To prevent UTIs, the most important thing is to reduce the chance of bacteria invading your urinary tract.
Urinate when you feel the need and never hold it in
Drink plenty of fluids and much more in hot weather. Any fluids count even tea and coffee.
Good genital hygiene keeping the region clean and dry.