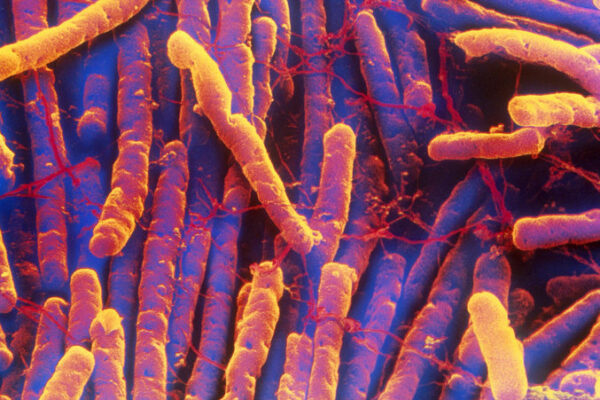
The sugar-rich Western diet is fuelling a superbug which has evolved to thrive in hospitals, scientists have warned.
The gut-infecting bacterium Clostrdium difficile(C.diff) is evolving into two separate species, with one group increasingly adapting to live in the guts of people with poor diets, while growing ever better at avoiding the harsh disinfectants used to clean wards.
More than 13,000 NHS patients each year are infected with C.diff, which can cause debilitating diarrhoea and leave sick people dangerously dehydrated.
Bacteria are also becoming increasingly resistant to antibiotics, and if not treated quickly enough an infection can be fatal. Nearly 2,000 people die from the bacterium each year in Britain.
Researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute and London school of Hygiene and Tropical medicine looked at the genetic differences of 906 strains of C-diff taken from humans and animals and the environment across 33 countries.
They found that a dangerous new species is rapidly emerging which can evade common hospital disinfectants and spread easily. And poor diets are making the problem worse.
Dr Trevor Lawley, the senior author from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, said: “Our study provides genome and laboratory based evidence that human lifestyles can drive bacteria to form new species so they can spread more effectively.
“We show that strains of C. diff bacteria have continued to evolve in response to modern diets and healthcare systems and reveal that focusing on diet and looking for new disinfectants could help in the fight against this bacteria.”
Researchers found that the new emerging species, named C. difficile clade A, made up approximately 70 per cent of the samples from hospital patients.
It had changes in genes that allow it to feed on simple sugars, and when tested in animals, it was able to colonise mice guts more thoroughly when their diet was high in sugar.
It had also evolved differences in the genes involved in forming spores, giving much greater resistance to common hospital disinfectants. These changes allow it to spread more easily in healthcare environments.
Dr Nitin Kumar, joint first author from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, said: “Our large-scale genetic analysis allowed us to discover that C. diff is currently forming a new species with one group specialised to spread in hospital environments.
“This is the first time anyone has studied genomes in this way to identify it.This particular bacteria was primed to take advantage of modern healthcare practices and human diets, before hospitals even existed.”
Encouraging people to change their diet or making sure hospital food is as healthy and sugar-free as possible could help to stave off infections, the study suggests.
The research was published in the journal Nature Genetics.
extract from Sarah Knapton, science editor Telegraph