There are 4 major vital signs and blood pressure is one of them-
The others are heart rate, breathing rate, and body temperature. These vital signs can help give a good idea of how well the body and its organs are performing.
Changes in vital signs can indicate an underlying health problem or a need to make lifestyle changes.
Blood pressure is measured using a blood pressure cuff. either at the GP or with a home testing kit.
What do the measurements mean?
Blood pressure measures the amount of force blood places on the blood vessels in the body. A blood pressure reading includes two numbers that indicate the pressure inside the arteries as the blood flows through the body.
The higher number is called the systolic pressure and this measures the pressure inside the arteries as the heart contracts to pump blood. The lower number is called the diastolic pressure and is the pressure inside the artery as the heart rests between each beat.
Normal blood pressure is anything below 120/80 mm Hg. If these numbers go higher than 120/80 mm Hg it is may be an indication that the heart is working too hard to pump the blood through the arteries around the body.
High blood pressure can be caused by many factors which include stress, high cholesterol and build-up of plaque in the blood vessels.
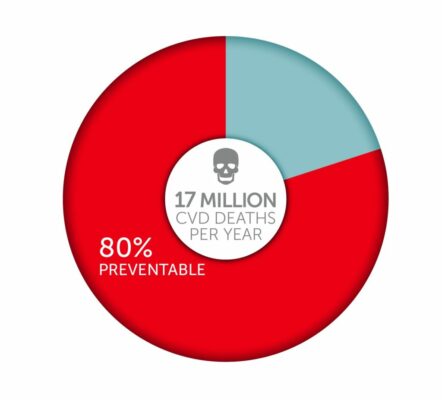
Accurate blood pressure readings are very important as high blood pressure may be totally silent and not cause any symptoms until it is dangerously high.
If you have high blood pressure the doctor may recommend checking and recording your blood pressure at home with your own machine. This will give them feedback on any changes during the day and after taking medications.
When checking blood pressure at home, it is important to remember:
- Manual cuffs come in different sizes depending on the size of the arm. Using the right size ensures the most accurate reading.
- The cuff should always sit directly on the bare skin.
- Take a few deep breaths and relax for up to 5 minutes before measuring blood pressure.
- Avoid talking during the test.
- Place the feet flat on the floor and sit up straight while measuring the blood pressure.
- Avoid checking blood pressure in a cold room.
- Support the arm as close to heart level as possible.
- Measure the blood pressure at a few different times during the day.
- Avoid smoking, drinking, and exercise for 30 minutes before taking blood pressure.
- Empty the bladder before taking a blood pressure test. A full bladder may give an incorrect blood pressure reading.
There are apps and wrist devices that claim to measure the blood pressure, but these results are frequently inaccurate and are not a reliable way to monitor a person’s health.
Apps that log blood pressure results may be helpful for people who need to take regular blood pressure tests, however.
Recording a set of readings into these apps may help doctors identify trends in blood pressure and recommend treatments.
Blood pressure status | Systolic mm Hg | Diastolic mm Hg |
Normal | Less than 120 | Less than 80 |
Elevated | 120–129 | Less than 80 |
Stage 1 high blood pressure (hypertension) | 130–139 | 80–89 |
Stage 2 high blood pressure | 140 or higher | 90 or higher |
Hypertensive crisis (seek immediate medical attention) | 180 or higher | 120 or higher |
Normal blood pressure is anything below 120/80 mm Hg. The numbers may change based on factors such as:
- age
- weight
- sex
- physical activity
- underlying medical conditions
Anyone uncertain about their target blood pressure should visit a doctor for guidance.
If you take your blood pressure at home and the reading is higher than usual then it is important to do another reading 5 minutes later to make sure it is accurate.
Anyone who experiences a systolic pressure over 180 mm Hg or a diastolic pressure over 120 mm Hg should seek emergency medical care as this is a sign of a hypertensive crisis.