Back pain is one of the most common reasons people go to the doctor or miss work, and it is a leading cause of disability worldwide.
Fortunately, you can take measures to prevent or relieve most back pain episodes. If prevention fails, simple home treatment and proper body mechanics often will heal your back within a few weeks and keep it functional. Surgery is rarely needed to treat back pain.
Back pain usually results from a problem with one or more parts of the back such as ligaments, muscles, nerves or the vertebrae. The most frequent cause would be what is described as Musculo-skeletal and generally settles in a few weeks. More rarely it can be caused by other internal organs.
Symptoms
Back pain can range from a muscle aching to a shooting, burning or stabbing sensation. In each case the pain can have different features. In some the pain is aggravated by standing, in others by sitting and occasionally some people are aggravated by lying. Some may be worse in the early mornings and others increase during the day. In addition the pain in some may radiate down the leg or worsen with bending, twisting or walking. The history and the behaviour of the pain will help the doctor and the physiotherapist to help diagnose the cause of the pain. So it is important to keep a note of how the pain behaves.
When to see a doctor
Most back pain gradually improves with home treatment and self-care, usually within a few weeks. Contact your doctor if your back pain:
- Persists past a few weeks
- Is severe and does not improve with rest
- Spreads down one or both legs, especially if the pain extends below the knee
- Causes weakness, numbness or tingling in one or both legs
- Is accompanied by unexplained weight loss
In rare cases, back pain can signal a serious medical problem. Seek immediate care if your back pain:
- Causes new bowel or bladder problems
- Is accompanied by a fever
- Follows a fall, blow to your back or other injury
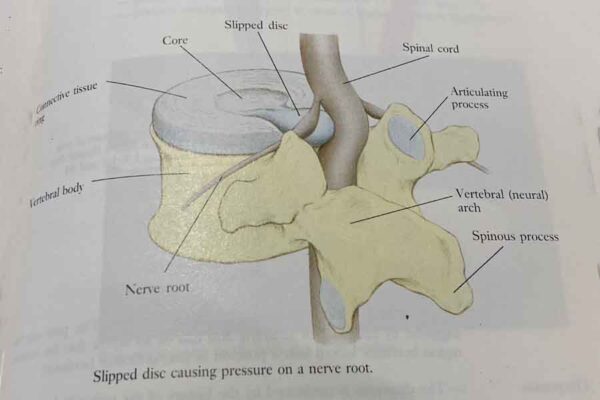
Back pain often develops without a cause that your doctor can identify with a test or an imaging study. Conditions commonly linked to back pain include:
- Muscle or ligament strain. Repeated heavy lifting or a sudden awkward movement can strain back muscles and spinal ligaments. If you sit all day in poor posture this can lead to postural strain which in turn can cause painful muscle spasms.
- Bulging or ruptured discs. Discs act as cushions between the bones (vertebrae) in your spine. The soft material inside a disc can bulge or rupture and press on a nerve. However, you can have a bulging or ruptured disc without back pain. Disc disease is often found incidentally when you have spine X-rays for some other reason.
- Arthritis. Osteoarthritis can affect the lower back. In some cases, arthritis in the spine can lead to a narrowing of the space around the spinal cord, a condition called spinal stenosis.
- Osteoporosis. Generally found in older people. The vertebrae become more porous and brittle and can easily develop small fractures.

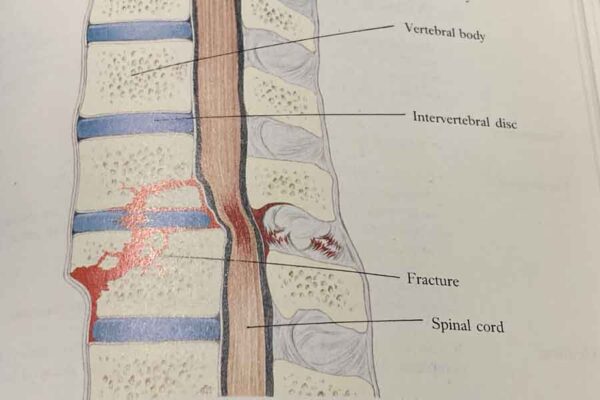
Risk factors
Anyone of any age can develop back pain, even children and teens. These factors might put you at greater risk of developing back pain:
- Age– Back pain is more common as you get older, starting around age 30 or 40.
- Lack of exercise- Weak, unused muscles in your back and abdomen might lead to back pain.
- Excess weight- Excess body weight puts extra stress on your back.
- Some types of arthritis and cancer can contribute to back pain.
- Improper lifting- Using your back instead of your legs can lead to back pain.
- Psychological conditions- People prone to depression and anxiety appear to have a greater risk of back pain.
- Smokers have increased rates of back pain. This may occur because smoking prompts more coughing, which can lead to herniated disks. Smoking can also decrease blood flow to the spine and increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Prevention
You might avoid back pain or prevent its recurrence by improving your physical condition and learning and practicing proper body mechanics.
To keep your back healthy and strong:
- Regular low-impact aerobic activities — those that do not strain or jolt your back — can increase strength and endurance in your back and allow your muscles to function better. Core exercises, pilates under the guidance of an experienced instructor and swimming are good choices. Walking is also a good general activity.
- Build muscle strength and flexibility.Abdominal and back muscle exercises, which strengthen your core, help condition these muscles so that they work together like a natural corset for your back.
- Maintain a healthy weight.Being overweight strains back muscles. Losing weight can prevent back pain.
- Quit smoking.Smoking increases your risk of low back pain. The risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked per day, so quitting should help reduce this risk.
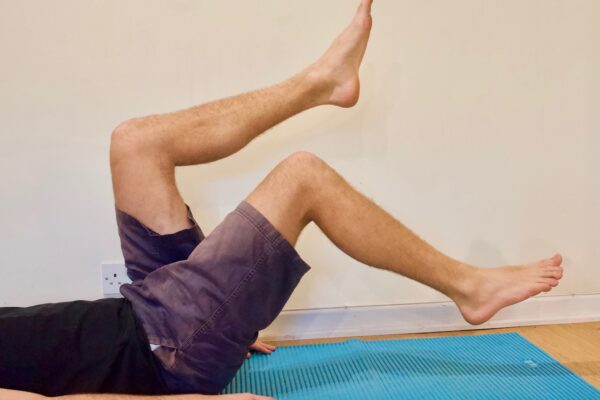
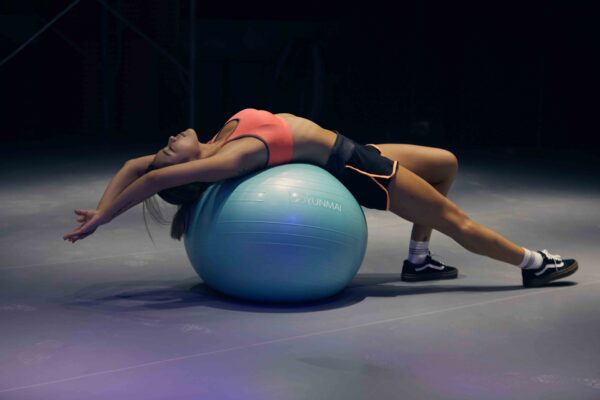
Try these exercises to mobilise and strengthen the back.
Back exercises- Basic mobilising
Avoid movements that twist or strain your back. Use your body properly:
- Stand tall- Try not to slouch. Maintain a neutral pelvic position. Good posture can reduce the stress on back muscles.
- Sit Well- Choose a seat with good lower back support, armrests and a swivel base. Placing a pillow or rolled towel in the small of your back can maintain its normal curve. Try and find a chair that allows you to sit with your knees and hip at 90 degrees and your feet on the ground. Change your position frequently, at least every half-hour.
- Lift carefully- Avoid heavy lifting, if possible, but if you must lift something heavy, let your legs do the work. Keep your back straight — no twisting — and bend only at the knees. Hold the load close to your body. Lift with someone else if the object is heavy or awkward.


Diagnosing back pain
You will have a physical examination where the doctor/ physiotherapist will look at:
- Range of motion of the spine
- Ability to stand and walk
- Reflexes
- Leg strength
- Altered sensation in the limbs
If the pain has been persistent and has not resolved over 6 weeks the doctor may send you for some tests such as blood and urine tests, X-ray, MRI, bone scan and in the case of nerve problems a EMG or nerve conduction test.
Treatment
- Take some regular simple analgesics such as paracetamol or neurofen. Take them regularly. In cases with severe spasm the GP can prescribe Diazepam which is a powerful muscle relaxant. They will only give you a few days supply as it is addictive but also does not work well over a longer period. Use the window in pain relief to try and move and to do some mobilising exercises. If you cannot take certain tablets try a topical anti inflammatory gel. See article on pain relief here-Tablets and Pain Relief
- Ice, heat or hot baths relieve the pain.
- Try to do some mobilising exercises little and often or some swimming
- Posture-Try to mix up your positions so do not sit too long or stand too long
- Wear comfortable rubber soled shoes or trainers that give a lot of shock absorbancy
- Check that your mattress is not old and sagging
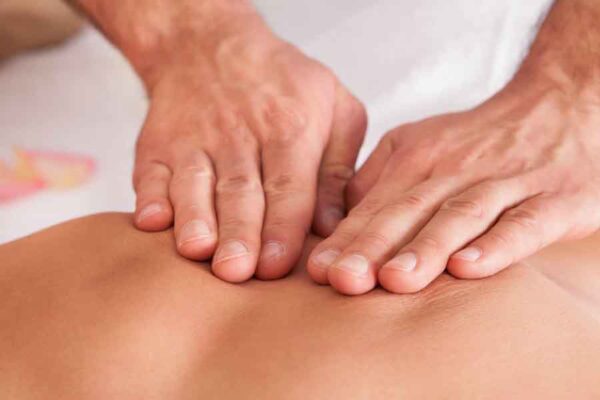
If none of the above are helping speak to your doctor.
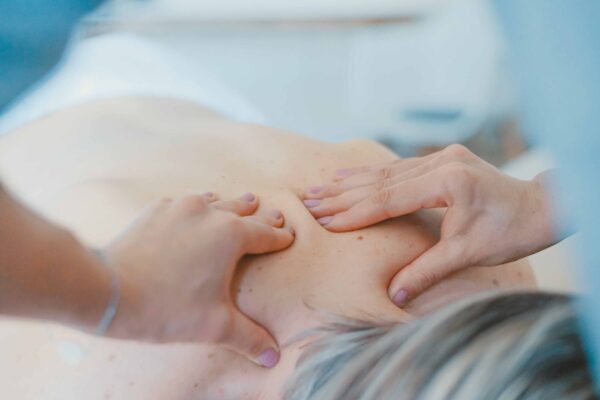
Manual Therapy
You should then try some manual therapy in the hands of a physiotherapist or osteopath.
The manual therapist will diagnose and treat the cause of the back pain by a combination of mobilising techniques and analyse which muscle groups needs strengthening and what needs stretching. You will be encouraged to do the correct set of exercises prescribed for you at home.
If after several weeks there is no progress you will need to go back to your doctor for an appointment.
The doctor may suggest a number of options with you
- Stronger drugs such as amitriptyline
- Further tests
- Steroid injection
- Be referred to a specialist who may suggest some form of surgery
With the advent of microsurgery this is not nearly as invasive as it was in the past and has a quick recovery time. This could be a number of options such as nerve decompression or micro-discectomy
Other treatments that can be tried are acupuncture, TENS machine

