This is a very broad term to describe any disorder that affects your joints. This can be caused by many different conditions the most common being wear and tear.
The symptoms can vary but usually involve stiffness, pain, swelling, occasional redness, warmth and a loss of the normal range of motion.
There are in fact over 100 types of arthritis with the most common being Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid arthritis. These should not be confused with each other
Rheumatoid arthritis –
is a systemic disease and affects the whole body including some organs.
It is what can be described as an auto-immune disease where the body starts to attack itself. This causes a chronic inflammatory condition which affects joints, tendons, tendon sheaths (fascia), muscles and bursa as well as other tissues throughout the body.
It is three times more common in women and often begins in 20-50 year olds.
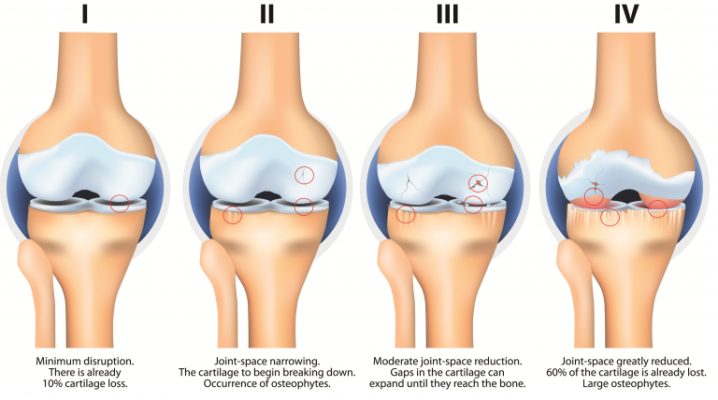
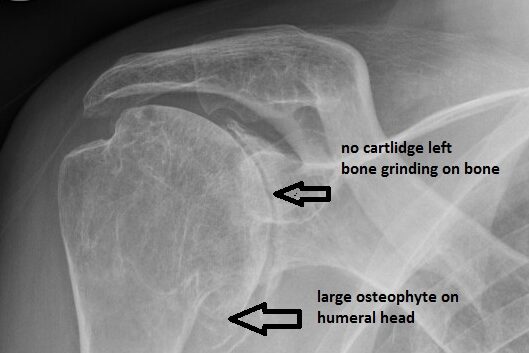
Osteoarthritis –
is basically wear and tear caused by ageing. This may be brought on prematurely by previous injury, being overweight, over use (for instance people who do hard manual work) and genetic disposition.
Osteoarthritis can affect any joint in the body. It most commonly affects the main weight bearing joints of the hip, knee, ankle and feet but also commonly affects the spine, neck, shoulder and hands.
The early signs of pain and stiffness with loss of range of movement can be treated well with physiotherapy. This can delay the need for an operation for many years, which may be advised by your consultant depending on the severity and your age.
In severe cases of arthritis in the hip, knee and shoulder a replacement is often done.
The smaller joints such as in the spine are best treated by gentle mobilisations combined with an exercise program to build up the muscles around to prevent strain. You may also be advised to take regular painkillers such as paracetamol and to lose some weight, which takes the strain off you weight bearing joints.

